Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, School of Physics and Electronic Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 Huawei Technologies Co, Ltd., Bantian Longgang District, Shenzhen 518129, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
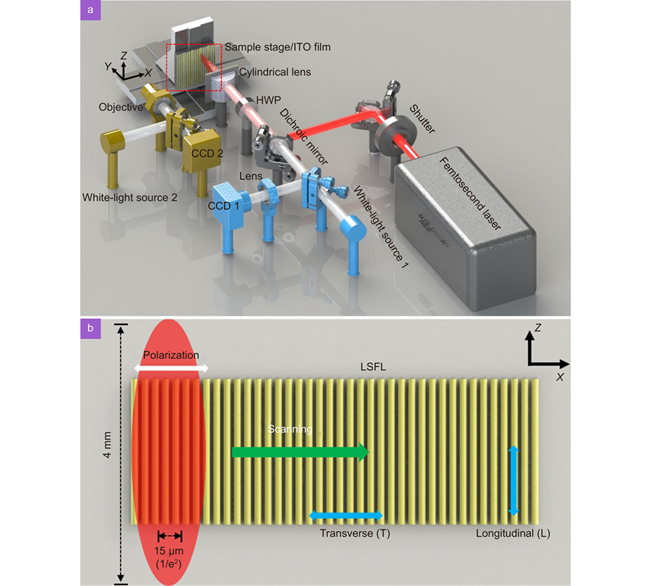
This paper reports the fabrication of regular large-area laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSSs) in indium tin oxide (ITO) films via femtosecond laser direct writing focused by a cylindrical lens. The regular LIPSSs exhibited good properties as nanowires, with a resistivity almost equal to that of the initial ITO film. By changing the laser fluence, the nanowire resistances could be tuned from 15 to 73 kΩ/mm with a consistency of ±10%. Furthermore, the average transmittance of the ITO films with regular LIPSSs in the range of 1200–2000 nm was improved from 21% to 60%. The regular LIPSS is promising for transparent electrodes of nano-optoelectronic devices—particularly in the near-infrared band.
transparent nanowires periodic surface nanostructures femtosecond laser direct writing ITO film anisotropic electrical conductivity Opto-Electronic Science
2023, 2(1): 220002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, School of Physics and Electronic Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Manipulations and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
Femtosecond laser ablation (FLA) has been playing a prominent role in precision fabrication of material because of its circumvention of thermal effect and extremely high spatial resolution. Molecular dynamics modeling, as a powerful tool to study the mechanism of femtosecond laser ablation, still lacks the connection between its simulation results and experimental observations at present. Here we combine a single-shot chirped spectral mapping ultrafast photography (CSMUP) technique in experiment and a three-dimensional two-temperature model-based molecular dynamics (3D TTM-MD) method in theory to jointly investigate the FLA process of bulky gold. Our experimental and simulated results show quite high consistency in time-resolved morphologic dynamics. According to the highly accurate simulations, the FLA process of gold at the high laser fluence is dominated by the phase explosion, which shows drastic vaporized cluster eruption and pressure dynamics, while the FLA process at the low laser fluence mainly results from the photomechanical spallation, which shows moderate temperature and pressure dynamics. This study reveals the ultrafast dynamics of gold with different ablation schemes, which has a guiding significance for the applications of FLA on various kinds of materials.
Ultrafast Science
2022, 2(1): 9754131

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, School of Physics and Materials Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Optical Instrumentation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
![]()
![]() Over the past two decades, femtosecond laser-induced periodic structures (femtosecond-LIPSs) have become ubiquitous in a variety of materials, including metals, semiconductors, dielectrics, and polymers. Femtosecond-LIPSs have become a useful laser processing method, with broad prospects in adjusting material properties such as structural color, data storage, light absorption, and luminescence. This review discusses the formation mechanism of LIPSs, specifically the LIPS formation processes based on the pump-probe imaging method. The pulse shaping of a femtosecond laser in terms of the time/frequency, polarization, and spatial distribution is an efficient method for fabricating high-quality LIPSs. Various LIPS applications are also briefly introduced. The last part of this paper discusses the LIPS formation mechanism, as well as the high-efficiency and high-quality processing of LIPSs using shaped ultrafast lasers and their applications.
Over the past two decades, femtosecond laser-induced periodic structures (femtosecond-LIPSs) have become ubiquitous in a variety of materials, including metals, semiconductors, dielectrics, and polymers. Femtosecond-LIPSs have become a useful laser processing method, with broad prospects in adjusting material properties such as structural color, data storage, light absorption, and luminescence. This review discusses the formation mechanism of LIPSs, specifically the LIPS formation processes based on the pump-probe imaging method. The pulse shaping of a femtosecond laser in terms of the time/frequency, polarization, and spatial distribution is an efficient method for fabricating high-quality LIPSs. Various LIPS applications are also briefly introduced. The last part of this paper discusses the LIPS formation mechanism, as well as the high-efficiency and high-quality processing of LIPSs using shaped ultrafast lasers and their applications.
laser-induced periodic structures (LIPSs) formation mechanisms femtosecond pulse shaping pump-probe imaging structural color birefringent effects optical absorption photoluminescence Opto-Electronic Science
2022, 1(6): 220005

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
2 Zhejiang Lab, Hangzhou 311100, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, School of Physics and Electronic Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
4 CAS Center for Excellence in Ultra-Intense Laser Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
Printing stable color with a lithography-free and environment-friendly technique is in high demand for applications. We report a facile strategy of ultrafast laser direct writing (ULDW) to produce large-scale embedded structural colors inside transparent solids. The diffraction effect of gratings enables effective generation of structural colors across the entire visible spectrum. The structural colors inside the fused silica glass have been demonstrated to exhibit excellent thermal stability under high temperature up to 1200°C, which promises that the written information can be stable for long time even with unlimited lifetime at room temperature. The structural colors in the applications of coloring, anti-counterfeiting, and information storage are also demonstrated. Our studies indicate that the presented ULDW allows for fabricating large-scale and high thermal-stability structural colors with prospects of three-dimensional patterning, which will find various applications, especially under harsh conditions such as high temperature.
ultrafast laser direct writing structural color glass information storage Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(3): 030501
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Inhomogeneity and low efficiency are two important factors that limit the application of laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSSs), especially on glass surfaces. In this study, two-beam interference (TBI) of femtosecond lasers was used to produce large-area straight LIPSSs on fused silica using cylindrical lenses. Compared with those produced using a single circular or cylindrical lens, the LIPSSs produced by TBI are much straighter and more regular. Depending on the laser fluence and scanning velocity, LIPSSs with grating-like or spaced LIPSSs are produced on the fused silica surface. Their structural colors are blue, green, and red, and only green and red, respectively. Grating-like LIPSS patterns oriented in different directions are obtained and exhibit bright and vivid colors, indicating potential applications in surface coloring and anti-counterfeiting logos.
Opto-Electronic Advances
2021, 4(12): 200036-1